Wireless Networking - 3
Wireless Networking - 3
Summary on What we have studied in last Tutorial :-
- IEEE 802.11 : Released in year 1997, this is the original version of 802.11 standard. It has a typical data rate of 1Mbps and maximum of 2Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band.
- IEEE 802.11a : Modified in the year 1999. this is the improved version of the original 802.11 standard. The 802.11a standard operates in the 5 GHz band and uses 52-subcarrier orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) for signal generation.
- IEEE 802.11b : This standard was also released in 1999. It has typical data rate of 6.5 Mbps and a maximum data rate of 11 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band. The media access method used here is also Carrier Sense Multiple Access with collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA).
- IEEE 802.11g : This standard was released in June 2003. It has a typical data rate 0f 22Mbps and maximum data rate 54Mbps in a 2.4 GHz band. The indoor range is 30 m.
- IEEE 802.11n : This is the latest version of IEEE 802.11 standard. It has typical data rate 300 Mbps and a maximum data rate of 600 Mbps in the 2.4 or 5 GHZ frequency band.
(3) Components used in Wireless Networking :-
Wireless device communication with the help of radio frequency waves. The important components required for setting up a wireless network are :
- Access Point
- Wireless router
- Extension point
- Antennas
- Wireless adapters
- Wireless station
- Server
(3.1) Medium :-
Wireless medium is an unguided form of networking medium. Signals are transmitted through air and space using Radio and Satellite networks. Satellite communication networks transmits and receives signals between earth and base stations and satellites located in space.
In a wireless transmission, transmitters and receivers are used to send and receive data. Both wired and wireless networks can be used together in a network. Wireless transmission uses Bluetooth, Infrared, Lasers, Radio Signals and Microwave technologies for data transmission. Lasers, Infrared and bluetooth are used mainly in LAN environments, whereas microwave and other radio frequencies are used to connect vast geographical locations. Mobile computing allows you to connect to any network either using bluetooth or Radio Frequencies.
(3.2) Access Point :-
A wireless access point (WAP) device is used to estabish a connection between two or more wireless devices. It is a device that bridges between a wireless connection and a wired connection. It is a hub that maintains data flow between wired and wireless network. Access points are used to add a wireless extension to the network. Access points include features like encryption. A basic WAP operates like a hub and works at layer 2. The figure shown below is wireless Access point :
Access point is a physical connection that is used to established a connection between a wired network and a wireless network.
Figure below shows the illustration of the wireless network connection using a hardware access point :
 |
| Wireless access point |
Access point is a physical connection that is used to established a connection between a wired network and a wireless network.
Figure below shows the illustration of the wireless network connection using a hardware access point :
 |
| Wireles Connection using Hardware Access Point |
(3.3) Wireless Router :-
A wireless router is simply a router with a wireless interface and incorporates the utilities of a wireless access point. It is generally used to permit acess to the internet to the wireless network users. It can work in a LAN (cabled), or only in wireless network, or a combination of both.
A wireless router consists of the folowwing :
- LAN ports : Used to connnect to a switch or LAN port of PC
- WAN port : It connects to WAN (wide area network) for internet connection
- Wireless antennas : The antennas are used to increase the range of the wireless network
Figure down below shows a wireless router :
 |
| wireless router |
(3.4) Extension Point :-
Extension points are used if a single access pont is not able to cover the entire area. Extension points act as wireless relays extending the range of wireless network Multiple extension points can alos be connected together to provide wireless acces to devices far away from the main access point. Figure below shows the use of extension point to connect wireless device :
 |
| Extension Point |
(3.5) Antennas :-
Antennas are used to increase the range of the wireless network. Antennas transmit signal in deifferent ways. While installing antennas ensure that the antenna is compatible with the router, access point or the adapter that you installed in the network. Figure below shows the antenna :
 |
| Omni-Directional Antenna |
(3.6) Adapters :-
Wireless adapters helps to connect the computer to a network. The wireless adapters are available as PCI card based or USB Card based. Some of the features available with wireless adapters are removable and retractable antennas, connection monitoring software and encryption support. The adapter should be checked for compatibility with the operating system. If the wireless adapter is used in a large area such as an organisation or office it should be compatible with the encryption schemes like WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy ) and WPA. The wireless network adapters are not only used in computeres but also used in network printers. The printers used wireless NICs or Bluetooth adapters. The wired NIC charge the network cable with the help of electric current or firing off light pulses whereas the wireless NIC transmitts and receives radio waves. This is the only difference between wired and wireless NIC.
Note :-
WEP and WPA are encryption standards used in wireless networks.
Figure below shows wireless adapter and dongle :
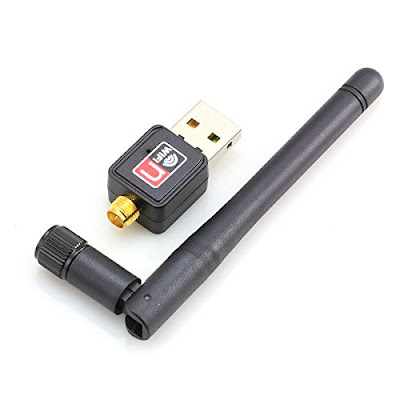 |
| Wireless adapters and Dongle |
(3.7) Wireless Station and Server :-
Wireless local area network consists of wireless station and wireless server. Devices that can connect to the wireless network using wireless mwdium are known as Stations. The station communicate with the help of wireless Network Interface Cards (NIC). Wireless NIC has to be installed in each of the stations. The station can be broadly classified into two categories. They are :
- Wireless Clients : Includes all wireless devices such as laptops, Presonal Digital Assistants (PDAs), Mobile phone and fixed devices such as PCs and Devices having Wireless NIC.
- Access Point : Access point acts as a base station within a wireless networks. They help in communication with the wireless devices by transmitting and receiving Radio frequency waves from the wireless devices.
Wireless server is the main server that is connected to the wired network which in turn is connected to the access points. It controls all the devices within the wireless networks.
Figure below illustrates the wireless Station and Servers :
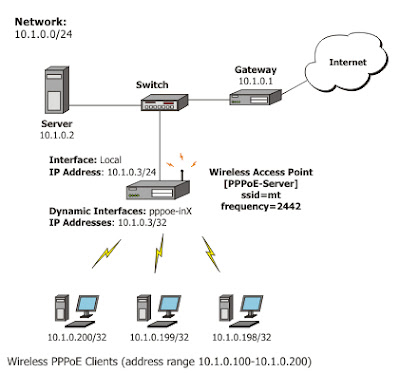 |
| Wireless station and server |
(3.8) Software :-
The wireless network adapter requires two types of software so as to funtion properly with an operating system (OS) that is a driver and configuration utility. The installation of drivers for wireless networking devices is similar to driver installations of any other hardware devices. Most of the OS had built-in drivers for many popular wireless NICs and these well equipped of wireless networking. However, it is better to use the driver and configuration utilities provided by the vendor along with the wireless adapter.
Along with the driver you also need a utility for configuring the wireless device. The browser base setup utilities are used to configure wireless APs and Routers.
=================================================
Thanks for reading !
Have a GOOD DAY !




Comments
Post a Comment